Describe the Second Portion of Photosynthesis
The interior space that surrounds the thylakoids is filled with a fluid called stroma. Which part of the plant gives it their green color.

What Are The Two Stages Of Photosynthesis Application Of Photosynthesis In Modern Technology Photosynthesis Light Reaction Photosynthesis Activities
The NADPH and the ATP created here go on to fuel the reactions in the second part of photosynthesis - The Calvin Cycle Describe how ATP is produced as a result of light striking chlorophyll molecules during the light dependent phase.

. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose. In the second stage ATP and NADPH are used to convert the 3-PGA molecules into molecules of a three-carbon sugar glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate G3P. The chemical equation in the light reaction of photosynthesis can be reduced to.
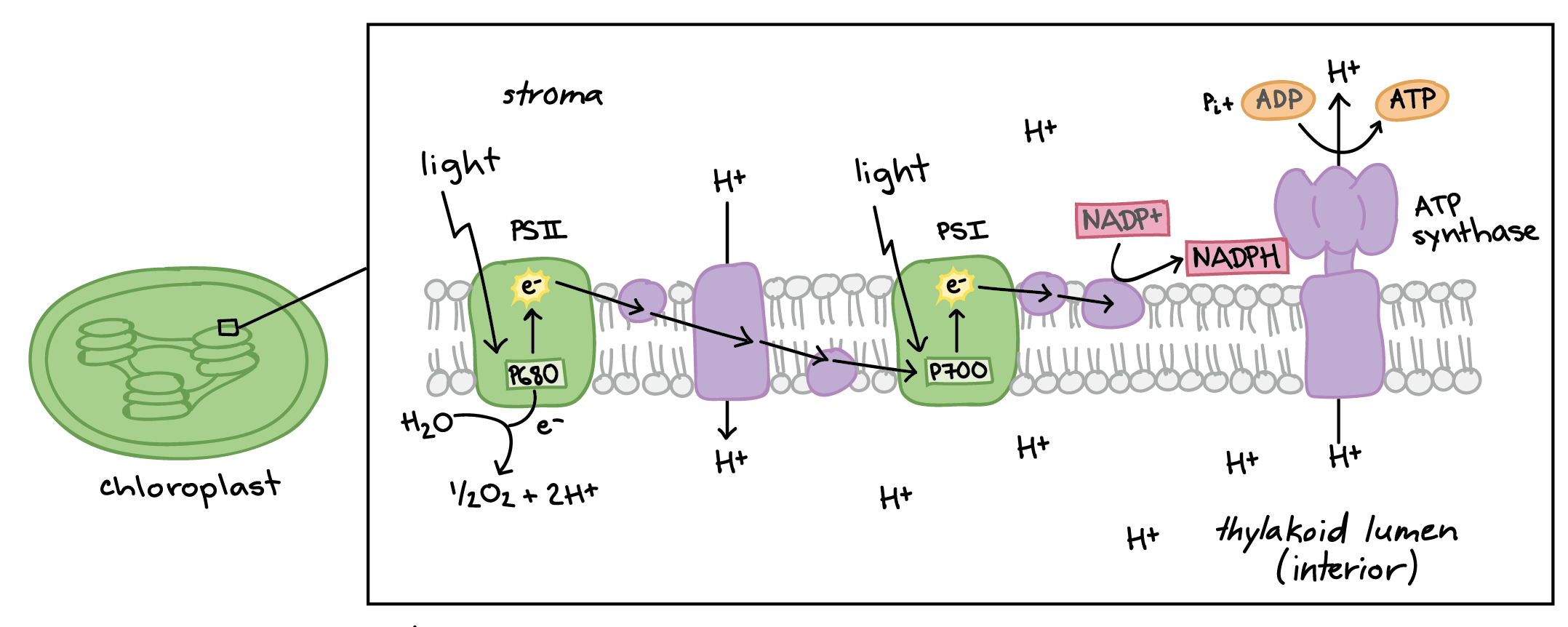
The interior space that surrounds the thylakoids is filled with a fluid called stroma. The process of photosynthesis is commonly written as. A photon strikes the antenna pigments of photosystem II to initiate photosynthesis.
The energy travels to the reaction center that contains chlorophyll a to the electron transport chain which pumps hydrogen ions into the thylakoid. The pigments of the first part of photosynthesis the light-dependent reactions absorb energy from sunlight. What is the main pigment found in plant leaves.
What are the raw materials used in. What process releases the least ATP per molecule of glucose for immediate cell use. Where does the second step of photosynthesis occur.
BThe second stage of photosynthesis is called the dark stage or light-independent stage. In the second stage the light-independent reaction takes place the Calvin cycle. This is where carbon dioxide is used to produce glucose the second part of.
In the first part of photosynthesis the light-dependent reaction pigment molecules absorb energy from sunlight. It collects energetic electrons from the first stage process which is powered through Photosystem II and uses the light energy to further boost the energy of the electrons toward accomplishing the final goal of providing energy in the form of reduced. During cellular respiration the complete breakdown of one molecule of glucose results in a maximum yield of 38 molecules of.
This is the site of the first part of photosynthesis. The second stage of photosynthesis is called the Calvin cycle. This is where carbon dioxide is used to produce glucose the second part of photosynthesis.
Light reactions take place first forming the photo portion of photosynthesis while the Calvin cycle follows completing the cycle with several steps involving photosynthesis. This is the site of the first part of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is defined as one process but contains two distinct stages which in turn break down into a series.
The most common and abundant pigment is chlorophyll a. This means that the reactants six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules are converted by light energy captured by chlorophyll implied by the arrow into a sugar molecule and six oxygen molecules the products. Photosynthesis is the process through which plants convert light energy from the sun to chemical energy.
A photon strikes photosystem II to initiate photosynthesis. While the mechanisms of photosynthesis are complex the overall reaction occurs as follows. Photosystem I makes use of an antenna complex to collect light energy for the second stage of non-cyclic electron transport.
Within the plant cell the water is oxidized meaning it loses electrons while the carbon dioxide is reduced meaning it gains electrons. Energy travels through the electron transport chain which pumps hydrogen ions into the thylakoid space. Calvin Cycle light independent reactions The second stage of photosynthesis.
The inner compartments inside the thylakoids are called the thylakoid space or lumen. Photosynthesis takes place in two stages the first phase is where the light reactions or the light-dependant reactions occur. The inner compartments inside the thylakoids are called the thylakoid space or lumen.
Under the light-dependent reactions the light energy is converted to ATP and NADPH which are used in the second phase of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll inside chloroplasts. Ferredoxin can then be used by the ferredoxinNADP reductase FNR enzyme to reduce NADP to NADPH.
Comprised of two stages one stage converts the light energy into sugar and then cellular respiration converts the sugar to Adenosine triphosphate known as ATP the fuel for all cellular life. Details of this step Regeneration. During photosynthesis plants take in carbon dioxide CO 2 and water H 2 O from the air and soil.
Describe the second stage of photosynthesis. A second light-driven reaction is then carried out by another chlorophyll protein complex called Photosystem I PSI. Lets have a look at the process of photosynthesis and also explore its importance.
However at photosystem II the energy derived from absorption of photons is used to split water molecules to molecular oxygen and protons see Figure 1022. The two stages of photosynthesis are light reactions and the Calvin cycle. 6CO 2 6H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2.
PSI oxidizes plastocyanin and reduces another soluble electron carrier protein ferredoxin that resides in the stroma. This stage gets its name because NADPH donates electrons to or reduces a three-carbon intermediate to make G3P. Therefore the Calvin cycle is the second phase of photosynthesis that mediates the synthesis of bioorganic compounds necessary for cell function and metabolism.
During the process of photosynthesis plants capture light energy and use it to convert water carbon dioxide and minerals into oxygen and glucose. Dark reaction utilizes ATP and NADPH energy molecules coming from the light reaction of photosynthesis for the regeneration of RuBP and carbohydrate synthesis. The conversion of unusable sunlight makes plants green.
Carbon dioxide sunlight. The second of two major stages in photosynthesis following the light reactions involving atmospheric CO2 fixation and reduction of the fixed carbon into carbohydrate. During the light reactions ATP and NADPH are generated by two electron-transport chains water is used and oxygen is produced.
The pathway of electron flow starts at photosystem II which is homologous to the photosynthetic reaction center of R.

A Simple Diagram Of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Activities Photosynthesis Projects

Light And Dark Reaction Light In The Dark Photosynthesis Study Biology
Light Dependent Reactions Photosynthesis Reaction Article Khan Academy
0 Response to "Describe the Second Portion of Photosynthesis"
Post a Comment